SewageGPT answers questions
Published: 2025-09-22
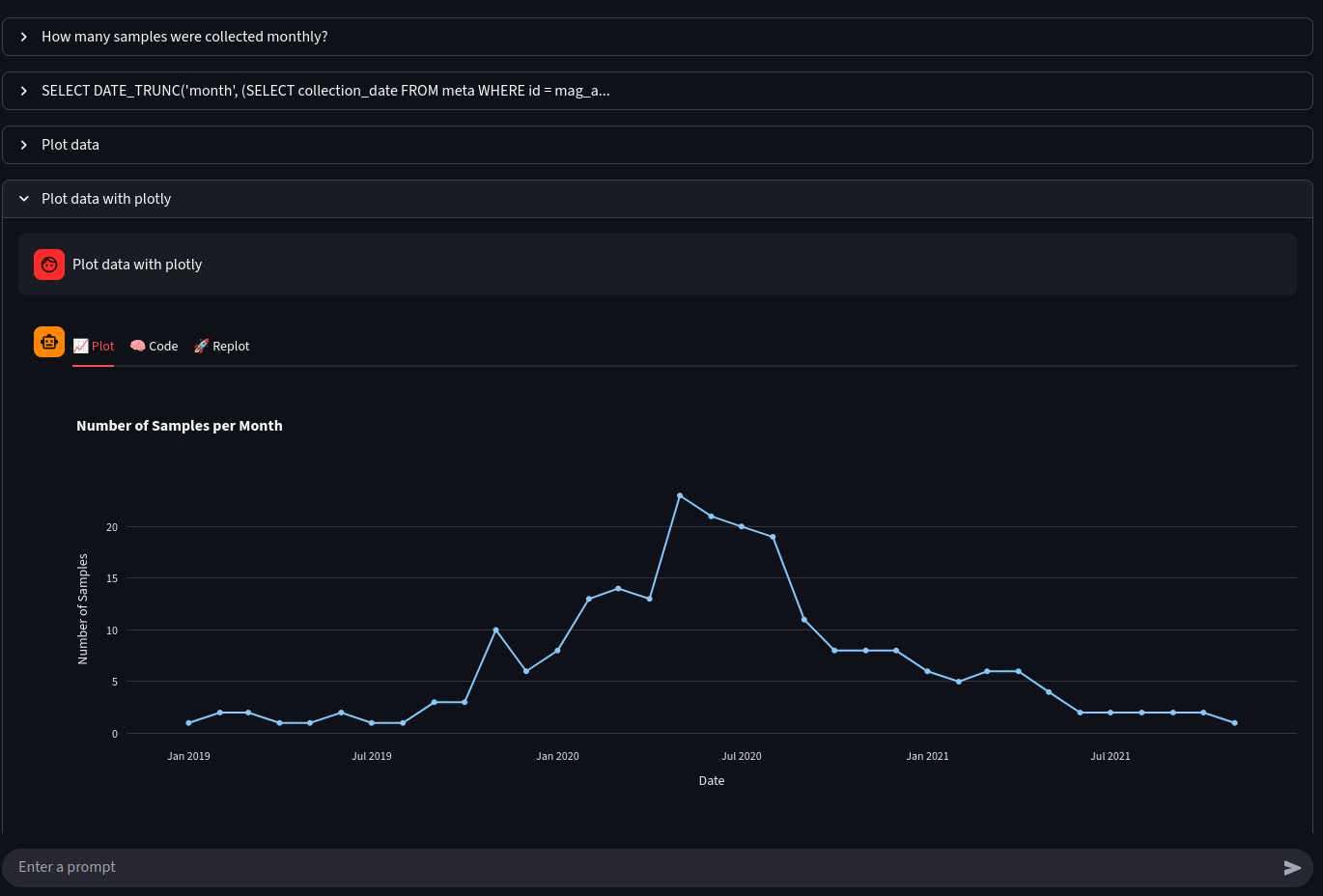
Relational databases offer an efficient solution for storing and retrieving complex data sets, yet the requirement for SQL programming expertise presents a significant challenge for many life science users. We explore whether a cutting-edge large language model can effectively translate plain English queries into SQL scripts (Text-to-SQL), thereby simplifying database interaction and eliminating the typical usage barriers. A complex database comprising 19 interconnected tables of metagenomic analyses from 239 sewage samples across five European cities was available. A large language model was provided with details of the database’s structure and background information on its contents. We evaluated the functionalities of this “SewageGPT” tool and assessed the accuracy of its responses to complex questions and visualisation of results. Providing a detailed description of the database enabled SewageGPT to accurately respond to complex inquiries, accelerating the database querying process. Knowledge of the database content proved beneficial, as it minimized the risk of ambiguities in queries; however, ambiguities can lead to incorrect responses. Therefore, human oversight remains crucial, particularly for questions that lack detail or involve ambiguities. The integration of state-of-the-art large language models with direct database connectivity substantially enhances the efficiency of query generation, statistical analysis and visualization of the results.